
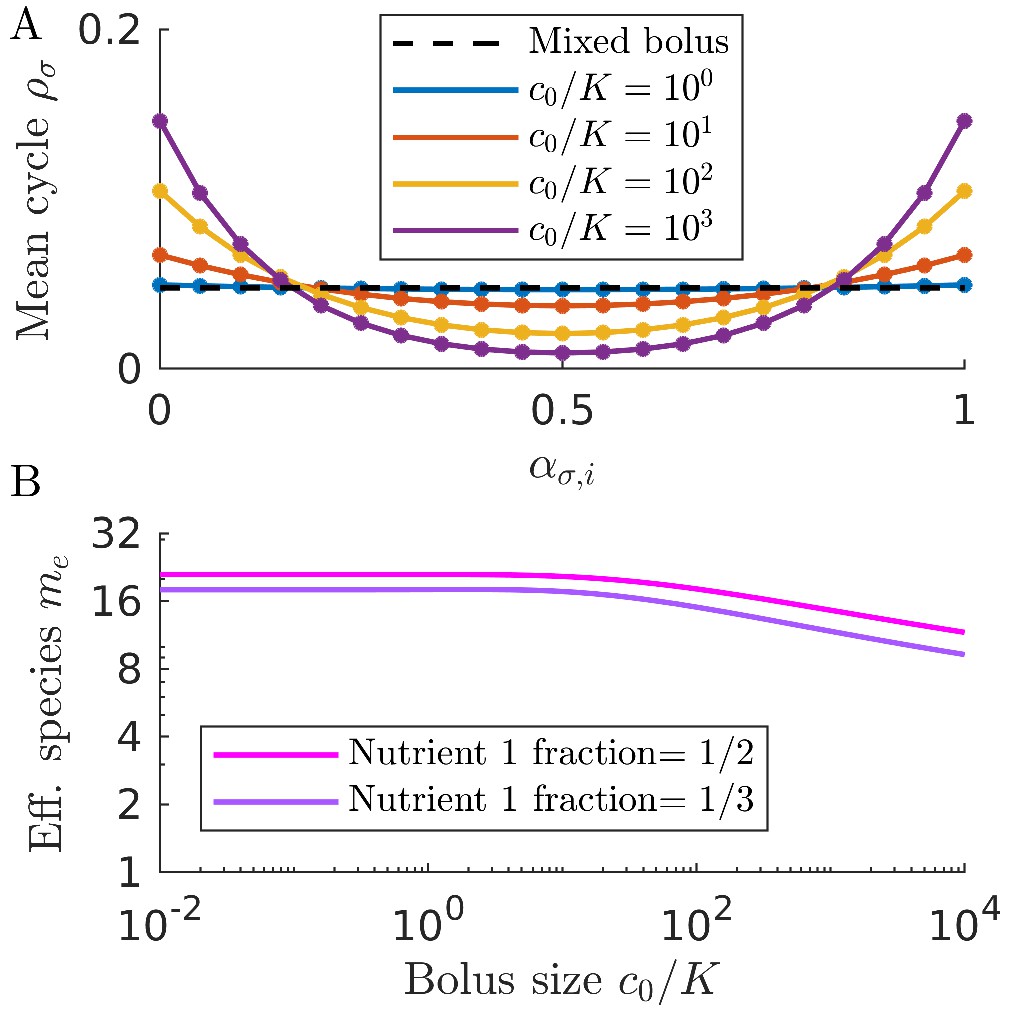

Water adjacent to hydrophobic regions is postulated to be more highly ordered than the bulk water. solute and ligand, to associate 10 (Figure 1).įIGURE 1: INTERACTION OF A SOLUTE WITH A TYPICAL REVERSED PHASE MEDIUM In this way, it is advantageous from an energy point of view for the hydrophobic moieties, i.e. Therefore, the degree of organised water structure is diminished with a corresponding favourable increase in system entropy. As solute binds to the immobilised hydrophobic ligand, the hydrophobic area exposed to the solvent is minimised. The initial mobile phase binding conditions used in reversed phase chromatography are primarily aqueous which indicates a high degree of organised water structure surrounding both the solute molecule and the immobilised ligand. The actual nature of the hydrophobic binding interaction itself is a matter of heated debate 9 but the conventional wisdom assumes the binding interaction to be the result of a favourable entropy effect. The separation mechanism in reversed phase chromatography depends on the hydrophobic binding interaction between the solute molecule in the mobile phase and the immobilised hydrophobic ligand, i.e. Molecules that possess some degree of hydrophobic character can be separated by reversed phase chromatography with excellent recovery and resolution 8. Theory of Reversed Phase Chromatography: Reversed phase chromatography has found both analytical and preparative applications in the area of biochemical separation and purification. The reasons for this include the simplicity, versatility, and scope of the reversed-phase method as it is able to handle compounds of a diverse polarity and molecular mass 5, 6, 7.
It is estimated that over 65% (possibly up to 90%) of all HPLC separations are carried out in the reversed-phase mode. Now a day reversed-phase chromatography is the most commonly used separation technique in HPLC due to its broad application range. Molecules that possess some degree of hydrophobic character, such as proteins, peptides and nucleic acids, can be separated by reversed phase chromatography with excellent recovery and resolution 4. Reversed phase chromatography has found both analytical and preparative applications in the area of biochemical separation and purification. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a chromatographic technique that can separate a mixture of compounds and is used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry to identify, quantify and purify the individual components of the mixture 3. Its power arises from its capacity to determine quantitatively many individual components present in mixture by single analytical procedure 1, 2. INTRODUCTION : Chromatography is probably the most powerful analytical technique available to the modern chemist. HPLC, RP-HPLC, Analytical methods, Chromatographic parameters This review covers the importance of RP-HPLC in analytical method development and their strategies along with brief knowledge of critical chromatographic parameters need to be optimized for an efficient method development. Molecules that possess some degree of hydrophobic character, such as proteins, peptides and nucleic acids, can be separated by reversed phase chromatography with excellent recovery and resolution. The reasons for this include the simplicity, versatility, and scope of the reversed-phase method as it is able to handle compounds of a diverse polarity and molecular mass. Now a day reversed-phase chromatography is the most commonly used separation technique in HPLC. IMPORTANCE OF RP-HPLC IN ANALYTICAL METHOD DEVELOPMENT: A REVIEWĭepartment of Pharmaceutical Analysis, Krupanidhi College of Pharmacy, Sarjapura Main Road, Carmelaram post, Bangalore-560 035, Karnataka, IndiaĬhromatography, although primarily a separation technique, is mostly employed in chemical analysis in which High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is an extremely versatile technique where analytes are separated by passage through a column packed with micrometer-sized particles.
Importance of serial dilution research full#
IMPORTANCE OF RP-HPLC IN ANALYTICAL METHOD DEVELOPMENT: A REVIEW HTML Full Text


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
